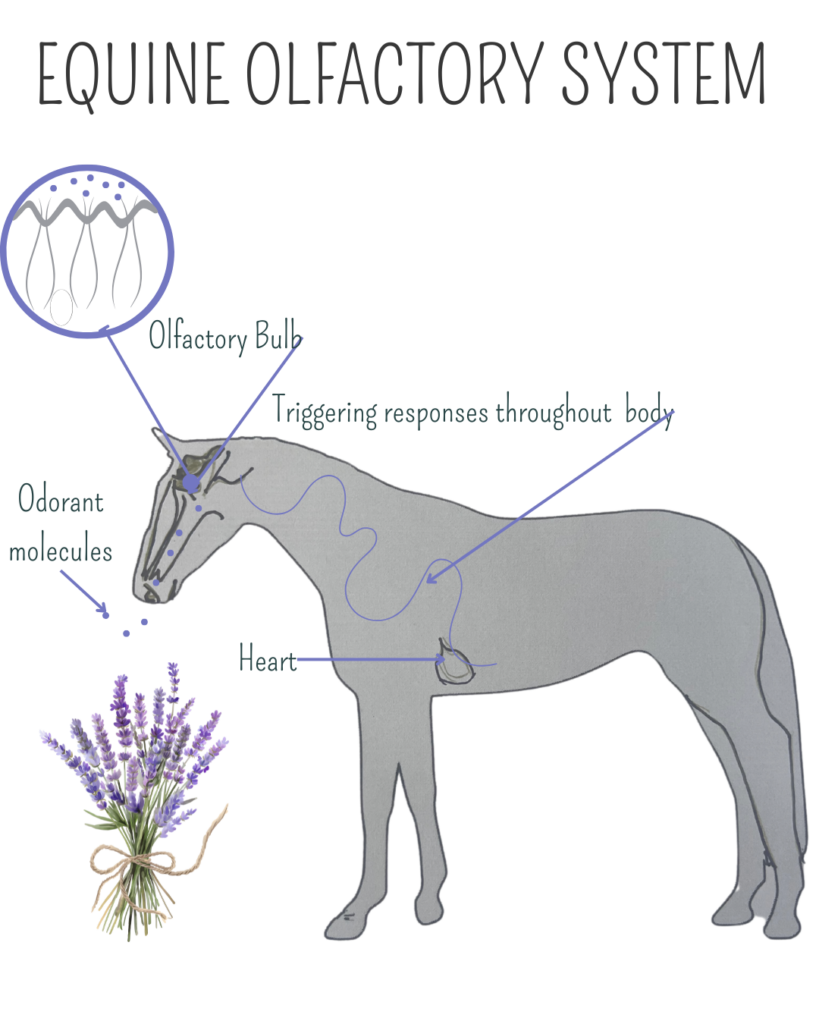
When you inhale lavender oil, the scent molecules enter your nasal cavity.
Inside your nasal cavity, there are specialized cells known as olfactory receptors. These receptors are sensitive to different scent molecules.
When lavender molecules bind to these receptors, they trigger a nerve impulse that sends signals to the olfactory bulb, a structure located at the base of the brain.
The olfactory bulb processes the signals and sends them to various areas of the brain, particularly:
Limbic System: This part of the brain is involved in emotional processing and memories. It is why certain scents can evoke strong emotional responses or memories.
Hypothalamus: This area influences physiological responses, including stress reduction, sleep regulation, and hormonal balance.
As the brain processes the scent, it triggers responses throughout the body:
Relaxation Response: Decrease in heart rate and blood pressure.
Mood Improvement: Release of neurotransmitters (like serotonin) that enhance mood.
Inhaling lavender aroma calms the horse’s brain, an effect measurable with heart rate monitors. Ann Baldwin’s study on HorseScents’ ScentStrap confirms that HorseScents effectively relaxes horses as indicated by heart rate monitors.
All Rights Reserved HorseScents, Inc. 2022